How To Easily Grow Tasty Vegetables At Home In Pots
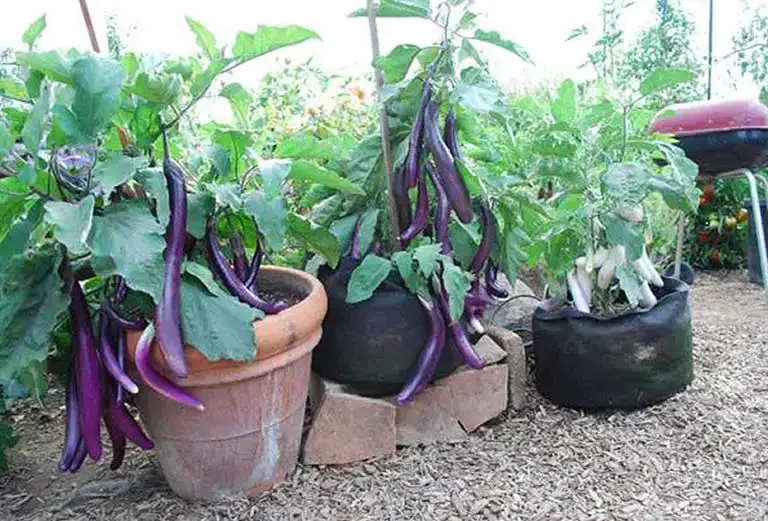

Most people who are new to the idea of urban agriculture tend to think growing vegetables is only available to people with a garden or an allotment but this is simply not true. There are a variety of different plants that grow quite happily in pots in cramped spaces and on window ledges or patios.
Table of Contents
- HOW TO GROW VEGETABLES AT HOME IN POTS
- HOW TO POT YOUR VEGETABLES FOR THE BEST RESULTS
- WHERE TO PUT YOUR POTTED VEGETABLES
- CARING FOR YOUR POTTED VEGETABLES
- 16 VEGETABLES THAT GROW WELL IN POTS
- PLANTING VEGETABLES IN THE SAME CONTAINER CAN SAVE SPACE
- WHEN & HOW TO HARVEST YOUR NEW POTTED VEGETABLES
- YOU SHOULD ALSO CONSIDER GROWIUNG FRUITS IN POTS
HOW TO GROW VEGETABLES AT HOME IN POTS
Vegetables don’t generally grow well indoors but there are some that will happily produce a harvest inside. However, as long as you have even a small amount of outdoor space, whether that be a patio or just the outside ledge of a window, there are really no vegetables that you cannot grow.
You only need a few simply materials to start and you can grow a variety of different vegetables at home in pots or other containers.
Let’s take a look at what materials you need, which vegetable plants grow best in pots and how to grow them.
6 Materials you need to successfully grow vegetables in pots
Let’s first look at the materials you need in order to successfully grow vegetables at home.
- Pots or containers.
- Soil.
- Seed, transplants or cuttings.
- Watering Can.
- Fertilizer.
- Outdoor space for growing (no matter how small).
The pot versus container debate
Ideally when growing vegetables at home you would want to grow them in fairly large sized containers or pots.
 A large deep container will allow the plants to form strong roots and grow bigger thus ensuring they bear much more produce.
A large deep container will allow the plants to form strong roots and grow bigger thus ensuring they bear much more produce.
However, not everyone has the space to use large containers or pots.
If you can use a larger medium sized pot or container then I advise you to do so but if that is not an option then you can use small pots or other container types. The harvest will be smaller but that shouldn’t stop you.
In truth you can really grow vegetables in any type of container than can hold soil.
Some people get very creative with their containers such as filling the center of laid out wheel, hollowed out tree trunks and even used shoes.
Follow the simple steps below to ensure you get the most from your home grown pot-vegetables. We will start by taking a lot at the essential materials you will need.
The soil you use is important
Choosing the soil for your pots is very important in home vegetable growing and it is something that is all-too-often overlooked by beginners.
Using standard garden soil in vegetable pots will only give you limited results – if any at all.
The container may not matter all that much but the soil sure does!
You need nutrient-rich soil that is prepared specifically to help grow and nurture new plants.
There are soils that are specifically prepared for growing from seed.
There are also soils that have been prepared specifically to grow plants from cuttings and other soils that have nutrients added which are specifically suited to vegetables.
Don’t get caught in the trap of buying an expensive soil though just because it states it is perfect for pot vegetable growing – look at the components of the soil mix and you may find that it has the same ingredients as the cheaper option!
Here are some types that I have found very useful.
A home made potting mix works best
A good potting mix is the very best type of soil to use when growing vegetables at home.
 A potting mix is a type of compost soil. It differs from garden soil in the fact that is prepared with all the necessary nutrients for growing plants, vegetables and herbs in containers.
A potting mix is a type of compost soil. It differs from garden soil in the fact that is prepared with all the necessary nutrients for growing plants, vegetables and herbs in containers.
The first recorded use of the “term potting soil” is from an 1861 issue of the American Agriculturist although the technique of growing plants and vegetables at home in pots dates back as far as Ancient Egypt.
A potting mix generally consists of:
- Typical garden soil – adds density and is a cheap source of bulk.
- Compost – contains billions of beneficial microbes.
- Sand or similar – for improved drainage.
- Peat moss – bulks up mixes without adding a lot of weight.
- Pine bark – lightens up soil to allow air and water to penetrate better.
- Perlite – this is a volcanic rock that holds up to 4 times its weight in water to main moisture in the pot, while it also increases pore space and improves drainage.
- Fertilizers – nutrients needed to help germinate seeds and develop healthy plant roots.
You can even prepare your own potting mix if you are a really “hands-on” type of person.
How much soil you need depends on the container/pot size
You need enough soil to fill each container up to a point about 1/2 inch to an inch below the rim.
As a rule-of-thumb you need:
- 1.7 liters (1/2 gallon) of soil per 6″ pot
- 13 liters (3 1/2 gallons) of mix per 12″ pot
- 23 liters (6 1/2 gallons) of mix per 20″ pot
Organic soil can work as long as it’s the right type
Many home gardeners prefer to use organic soil.
In reality organic soil is just the same as potting soil – as long as you don;t live in an arid area or a tropical or subtropical climate zone (see our guide to this here)..
You can get generic potting and organic soil or ones that have fertilizers added that are specifically beneficial to vegetables.
Why I use Miracle Gro soil & why you should to
Miracle grow potting mix, as well as the plant food, is fantastic for plants of all varieties not just vegetable plants.
 Although there are many different types of organic, nutrient-rich soils on the market I mention Miracle Grow only because I have had a lot of success using it.
Although there are many different types of organic, nutrient-rich soils on the market I mention Miracle Grow only because I have had a lot of success using it.
In cases where I just could not get certain plants to sprout from seed, even when I first treated the seeds (more on that later), I eventually had success using miracle grow soil – on every occasion!
There are other brands of soil on the market that are similar and that will probably give the same results but I have had no direct experience with them and therefore can advise you on their effectiveness.
Feel free to try different brands if you wish but I will be sticking to miracle grow until experience tells me to do otherwise.
You can pick up miracle grow at your local store or source it from Amazon.
HOW TO POT YOUR VEGETABLES FOR THE BEST RESULTS
When using post to grow vegetables you have the same seasonal limitations that you would have if you were to grow an entire field of them.
So, plant your vegetable pots the same time you would plant them if you were planting them in a garden.
The time for planting also depends on whether you want to grow from seed or cuttings.
First prepare the container or pot
Make sure your pot has at least one hole at the bottom to allow for water drainage.
 If you are using “creative containers” then be sure to drill some holes at the bottom.
If you are using “creative containers” then be sure to drill some holes at the bottom.
Regardless of whether you are planting from seed, transplanting an already grown plant or using cuttings from another plant, you must thoroughly water the soil in the pot before you begin. Make sure you soak the potting mix or organic soil completely.
Allow the container to sit for a few hours so the excess water drains out.
How to seed vegetables in a pot
You can start growing from seed indoors until your plants sprout and start to grow at which point you will usually need to move them outdoors unless you are growing a variety that is happy indoors.
Plant the seeds according to the package directions making sure you get seeds that appropriate for the season you plan to start planting in.
Because not all seeds will germinate you should plant more than you need – you can always remove excess plants later and transplant them in new pots.
You must prepare the seeds before planting to increase the germination rate
You can help increase germination by nicking the seeds and then soaking them in a cup of hydrogen peroxide and water solution.
Nicking the seeds helps with hydration
Nicking seeds can help them to germinate because it helps the seeds absorb water better. The absorbed water then signals the plant embryo inside the seed shell to begin the process of germination.
Nicking plant seeds and then soaking them in a hydrogen peroxide water solution will greatly increase the germination of your seeds (explained below).
 Nicking seeds is a very simple process but is monotonous and time-consuming.
Nicking seeds is a very simple process but is monotonous and time-consuming.
Simply take a sharp knife or razor blade and carefully cut or nick a corner of each seed.
Just a simple small nick at the side or corner of the seed is all that is needed. You should be careful not to cut deeply into the seed as you can damage the embryo inside.
Please be careful when doing this as nicking seeds has lead to many cut fingers and hands due to a lack of concentration.
An alternative to nicking seeds involves the use of sandpaper. Simply sand a spot on the seed until you expose the seed germ inside. Sanding is safer than nicking but is even more time-consuming.
Soaking the seeds in a homemade solution is the secret sauce to increased germination numbers
 Once you have nicked the seeds you should place them in a solution of watered hydrogen peroxide.
Once you have nicked the seeds you should place them in a solution of watered hydrogen peroxide.
Prepare the solution with the following ratio:
- 1 teaspoon of 3% hydrogen peroxide (like this one on Amazon)
- One quart of water
Mix as much as you need for soaking your seeds using the ratio above.
Soak for 12 hours.
How to pot vegetables from plant transplants
This is very straightforward.
Just take the plant that has already grown and plant it in your pot making sure the roots are at least a few inches below the the top soil in your pot.
Place about an inch of soil in the bottom of your pot and set transplants at the same level they were growing in their pot (except for tomatoes, which you can pinch off their lower leaves and plant them deeper in the container).
Put the transplant in the middle holding it upright as you fill the space around it with new soil.
Compact the soil down well so the plant is secure and then water it.
You can usually get vegetable plant transplants for a local nursery or garden center.
How to pot cuttings to cultivate new vegetables
If you are growing plants from cuttings you should start planting them around the time these vegetables would be growing if you had grown them from seed, which is usually several weeks later than you would plant from seed.
If you are using a cutting you will want to use a root solution to encourage the cutting to grow roots.
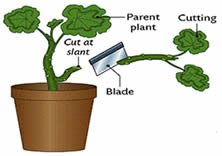 Before I plant a cutting I will make sure the end (that gets planted) is cut at an angle and first dipped into a rooting gel, such as Clonex
Before I plant a cutting I will make sure the end (that gets planted) is cut at an angle and first dipped into a rooting gel, such as Clonex, and then also dipped into a rooting hormone powder like TakeRoot
.
This may seem like overkill, using two different rooting compounds, but it really does make a difference to your overall success rate at growing healthy plants from cuttings.
Place cuttings at a depth of about 1 to 1 ½ inches and 2″ to 6″ apart..
WHERE TO PUT YOUR POTTED VEGETABLES
Most vegetables plants require a minimum of six hours of sunlight per day.
Of course there are some vegetable plants that can get by on less sunlight, such as salads and herbs, while there are others that grow best when they get a lot of sunlight, such as tomatoes and peppers.
 If the place you intend to grow your vegetables doesn’t get much sun then consider putting your plant pots on a dolly so you can move them to different spots as the sun changes.
If the place you intend to grow your vegetables doesn’t get much sun then consider putting your plant pots on a dolly so you can move them to different spots as the sun changes.
Also be aware that the wind is another factor to consider when you choose a place for your vegetable pots.
Protection from the elements is key
Your vegetable plants will be grow better when they are placed in a location that is protected from strong winds which can batter them and dry out their foliage.
 Just using the natural shelter offered by a nearby building is usually enough.
Just using the natural shelter offered by a nearby building is usually enough.
If there is nothing close by that would offer the plant shelter then you can erect a temporary windbreaker made from anything you have to hand.
The location must also provide the right type of light
You can also arrange your pots so that larger plants shield smaller plants – as long as they do not rob them of sunlight.
Place plants with similar light needs together and in the appropriately lit location.
Clustering potted plants together will also help to raise local humidity levels.
CARING FOR YOUR POTTED VEGETABLES
By far the most important thing to consider in vegetable pot care is watering.
You must inspect your vegetables regularly to make sure the potting mix hasn’t dried out.
You should not over-water your vegetable plants wither though as too much water can be as bad as too little.
Fertilizer is also another key consideration when growing plants of any kind in pots. Pots offer a very limited growing space and thus they offer a limited amount of nutrients that can and will get depleted fairly quickly.
Let’s take a look at watering and fertilizing a bit closer.
Your watering routine must be right
Vegetable plants require a consistent supply of water to grow well.
Low moisture levels in the soil is one of the biggest reasons for low harvest yield due to poor root development and over-watering s the biggest cause of root rot.
The best way to make sure your vegetable plants have the right amount of water is to use a self-watering planter.
Filling the reservoir every few days is all that’s required. The plants can then absorb moisture as they need it.
If you don’t have the space to use such a device then follow the instructions for watering each type of vegetable being aware that some plants will require watering more often or less often than others.
Fertilizing at the right time is important for stimulating vegetable growth
If you are using a potting mix or similar soil then you will not need to fertilize your plants for the first month or two as the soil has all the nutrients the plants need to thrive.
However, fertilization of vegetables in pots is important because they are growing in such a small confined space that even nutrient-rich soil will find its nutrients depleted quickly.
Once the plants have started to grow, and when they start to bear fruit, such as with tomato plants, once per week feed them with a water-soluble fertilizer.
If you are not using a potting mix then you should feed your vegetables about a month after planting them.
Checking for disease & removing bugs should be an ongoing activity
Although vegetable plants in pots and other containers aren’t as susceptible to disease and pest infestations as those growing in the ground (because they are physically separated from one and other and the disease can’t spread as easily) they can still be attacked.
 Remove or treat any plants that show signs of disease.
Remove or treat any plants that show signs of disease.
Disease in vegetables is too extensive a topic to cover in this article but you should be aware of the potential damage it can cause to your pot plants and know how to treat them.
If there is insect damage and/or eggs on the leaves of your plant try to avoid using environmentally-damaging over-the-counter bug killers (especially those from Monsanto) and instead simply wipe the leaves with soapy water and a cloth.
There may be times when you need to treat the plant with something stronger, if for example the roots are being attacked. Just be sure you use an organic compound like this one.
16 VEGETABLES THAT GROW WELL IN POTS
You can have a go at growing any type of vegetable you want in a pot but there are some that are more suited to this type of environment.
If this is your first time attempting to grow vegetables at home then you should consider taking the easy route before tackling more difficult-to-grow varieties.
Beans
Bean plants are climbers that like to grow up rather than out. If you plan to grow beans you will want to place your pots near some type of trellis or a similar structure that will offer the growing plant support.
Beans grow great in pots and need very little tending to. You can expect to see your first beans in just a few weeks after planting.
Bean plants need sun and a pot that has at least 12″ of soil depth.
Tomatoes
Tomatoes grow incredibly well in pots. In fact they grow so well in small containers that you can even grow them in grow-bags and hanging baskets.
 Bush tomato varieties or trailing varieties are the best best for pots.
Bush tomato varieties or trailing varieties are the best best for pots.
Be sure to plant cuttings, transplants and young plants in large containers around May after the risk of frost has passed. If the weather turns cold you can bring them inside until it warms up a bit or alternatively cover with a fleece at night and in very cold spells to help blanket in the heat and fend off the cold.
Tomatoes need to be watered regularly and will also respond well to fertilizer that is high in probiotic soil microbes and mycorrhizae such as you get in
Dr. Earth Home Grown (which is also good for growing all kinds of vegetables).
Peppers
Both peppers and chili peppers grow really well in pots.
They need plenty of sun and warmth. These are great candidates for growing on a sun-facing inside window sill.
They should be growing in a pot that has at least 12″ of soil depth and will require fertilizer if you want the plant to give you plenty of produce.
Peppers also respond very well when they are fertilized regularly.
Beetroot
Beetroot is another vegetable that grows well in pots.
Beetroot grows fast.
You can stagnate the sowing of seeds by sowing some seeds every few weeks. Doing this will mean you get a constant supply of beetroot throughout the summer months without having to wait for a one-off harvest time.
 If you don’t use the germination method mentioned above, in the soaking section, then soak your beetroot seeds in warm water for several hours before planting as this will encourage them to sprout.
If you don’t use the germination method mentioned above, in the soaking section, then soak your beetroot seeds in warm water for several hours before planting as this will encourage them to sprout.
You can sow up to 3 seeds together at a depth of about 1 inch. If you plan to plant more than 3 then keep the next set of 3 about 4 inches away from the first set.
Beetroots are considered a thirsty crop so they need a lot of water. However, it’s important to avoid over watering them. Too much water can lead to disease and insect infestations, and possible complete plant failure.
As a rule-of-thumb don’t let your beetroot plants dry out and follow the instructions given with your plant or seeds.
Once the vegetables are the size of golf balls you can harvest them.
Lettuce
Lettuce is a one of the easiest vegetables to grow in pots.
Just sow one or two seeds in a pot about 3/4 of an inch to 1 inch deep. Like beetroots you can stagnate the sowing of seeds so you have constant harvests rather than just one.
Lettuce plants require plenty of water. Do not let the soil dry out and make sure the soil you use is nutrient-rich.
Radish
You will be harvesting radish in as little as one month after you plant them in your pots.
 Growing radishes is recommend for beginners as they are almost completely hassle-free.
Growing radishes is recommend for beginners as they are almost completely hassle-free.
Just start by sowing your radish seeds at a shallow depth of about 1 cm deep making sure each of the seeds are at least 1 inch away from each other.
Radish also grows quickly and you can harvest after about a month. So, this is also a great vegetable to stagnate your planting so you can have a constant supply throughout the growing season.
Spinach
Spinach thrives when grown in pots and other containers.
It also does not require a lot of direct sun and will grow very well in partial shade. This means you can easily grow spinach indoors if you have limited outdoor space.
You only need a pot that is between 6″ and 8″ inches deep. You should choose a wide pot rather than a very deep one.
Sow the seeds about 1/2 deep with at least a 3″ separation between each seed.
They will usually start to germinate in less than a week and no longer than 2 weeks depending on the variety and growing conditions.
Peas
 Peas thrive in moderate conditions and grow quite happily in small pots.
Peas thrive in moderate conditions and grow quite happily in small pots.
They require very little attention apart from regular watering as they love moist soil.
When you source your pea seeds look for dwarf or bushier type varieties as they will give you a much better harvest when you sow them in pots. They also grow well indoors.
Sows seeds about 1″ deep.
They require sunlight so don’t put them in a very shaded area.
Many home gardeners prefer to germinate their pea seeds in small containers before replanting them in bigger pots once they start to grow.
Carrots
Unlike most of our previous vegetables carrots need deep soil to grow well so you will need to use deep pots if you want to grow this vegetable.
However be aware that although you can grow any type of carrot at home there are certain “stump-rooted” carrots that grow better in pots and containers like the Shin Kuroda variety.
If you choose a stumped-root variety (which are very tasty by the way) then you only need to sow the seeds 1/2” deep and 1/2” apart.
Depending on the growing conditions the seeds will begin to sprout anywhere from 6 days to 3 weeks.
For a continuous harvest throughout the growing season be sure to sow seeds every 2 – 3 weeks.
Cucumber
Cucumbers are mostly made of water and not surprisingly are a thirsty crop. They require regular watering.
 You will need to sow cucumber in a medium to large sized pot and place it in an area that gets plenty of direct sun.
You will need to sow cucumber in a medium to large sized pot and place it in an area that gets plenty of direct sun.
If you only have shaded areas to grow in or areas that get limited sun then you may be better skipping this vegetable.
They are usually ready to harvest in just a few months so you will also want to stagnant your sowing so you have a constant supply.
Squash
Squash is such an easy to grow plant and a big favorite with vegans like myself because it is such a versatile vegetable to cook with.
Summer squashes, such as Zucchini, tend to be more productive than winter squash types.
Squash is a great pot-vegetable for growing on rooftops, balconies and patios where there is plenty of sunlight.
Two very important things to consider when growing squash is the container size and the soil type. Just 1 squash plant can fill a 24″ pot very quickly.
You can learn more about growing squash at home here.
Eggplant
Growing eggplants is extremely easy. Eggplant is actually easier to grow in a pot than it is to grow in the garden!
 But, just like us humans, nasty little vegetable munching pests love the taste of eggplant, so this vegetable is very susceptible to garden pests. You will want to keep a close eye on your eggplants for any signs of an attack.
But, just like us humans, nasty little vegetable munching pests love the taste of eggplant, so this vegetable is very susceptible to garden pests. You will want to keep a close eye on your eggplants for any signs of an attack.
Eggplant is a heat-loving plant that requires high temperatures both day and night.
If you live in a warm climate you can grow it year round but if you live in a moderate or cold climate you may fin it difficult to get a good harvest from your work except at the height of summer.
You must keep your pots in direct sunlight and feed them regularly much more than you would for most other vegetable plants.
If you use a large pot with a 5 gallon capacity you can grow about 3 plants together. Make sure each plant will have at least 12 to 14 inches of space to grow fully though.
Make sure you water them regularly.
Chard
Chard is a cold weather crop that is simple to grow.
Chard grows very well in small sized pots.
However be aware that each plant needs at least 6″ of space to grow properly.
Water regularly.
Kale
Kale is also a cold weather crop but very easy to grow.
 Kale should be planted in full sun in colder regions and in partial sun in warmer regions.
Kale should be planted in full sun in colder regions and in partial sun in warmer regions.
Sow kale in a wide pot with a diameter of at least 12″. Just one plant per pot.
If you are using very large pots you can sow multiple kale plants in the same pot but make sure you plant them at least 12″ apart.
They require regular watering.
Garlic
Garlic bulbs grow great in pots and containers and what many people don’t know is that garlic greens can be eaten too. You can use the green leaves in salads and they taste great.
For garlic you need a pot that is 6″ to 8″ inches deep but that is very wide.
Give each bulb a space of about 6″ from the next bulb and plant them about 1″ deep.
Garlic takes a long to mature and you can expect to wait about 9 months before you can harvest.
Okra
 Okra is a warm season crop that requires heat and sunlight.
Okra is a warm season crop that requires heat and sunlight.
If you make sure the plant is placed in direct warm sunlight and fertilize it regularly you will get a bountiful harvest.
Although you can grow any type of Okra in a pot dwarf okra varieties will thrive in pots and give you a much better harvest.
The easiest vegetables to grow in pots for beginners (video)
Combing vegetable plants that also grow well in pots
Consider planting your vegetables in combinations.
 For example some food lovers plant Italian style combinations with specific herbs like basil and thyme growing with tomatoes or they may have a summer salad combination of tomatoes, beetroots, kale and lettuce growing together.
For example some food lovers plant Italian style combinations with specific herbs like basil and thyme growing with tomatoes or they may have a summer salad combination of tomatoes, beetroots, kale and lettuce growing together.
PLANTING VEGETABLES IN THE SAME CONTAINER CAN SAVE SPACE
You can even plant certain different vegetables in the same pot.
Just be aware that some vegetables will thrive together while others will die together.
Plants that thrive together
- Beans, carrots, squash
- Beans, summer savory, kale, celery
- Eggplant, beans
- Tomatoes, basil, onions
- Lettuce, herbs
- Spinach, chard, onions
Plants that die together
- Beans and onions or garlic
- Carrots and dill or fennel
- Tomatoes and squash
- Onions and beans or peas
WHEN & HOW TO HARVEST YOUR NEW POTTED VEGETABLES
Harvesting your lovely vegetables in the final step in the process (before you begin it again) and arguably it is the most rewarding part of the process.
 One of the most difficult parts of growing vegetables at home in pots for new gardeners is knowing when to harvest.
One of the most difficult parts of growing vegetables at home in pots for new gardeners is knowing when to harvest.
It may seem counter-intuitive but harvesting too early is not the biggest cause of poor harvest.
The biggest mistake many home gardeners make is waiting too long to harvest
As a rule-of-thumb you should aim to harvest your home grown vegetables when they look good enough to eat.
Most vegetables are more productive if you harvest early and often. Allowing your veg or fruit to stay on the plant too long will actually reduce harvest loads on the next growth cycle.
Last but not least, make sure you enjoy the entire process of growing vegetables at home in pots, as well as enjoying actually eating the harvest!
YOU SHOULD ALSO CONSIDER GROWIUNG FRUITS IN POTS
You don’t have to limit yourself to growing vegetables in pots at home. You can also grow fruit.
For a list of the best fruits to grow at home in pots read this article.
Herbs can also be grown in pots at home
Although they are not strictly speaking vegetables, herbs are a must-have edible plant for any home gardener.
Most herbs will grow quite happily in pots placed on a kitchen windowsill, patio or window ledge.
They are incredibly easy to grow. Just follow the instructions on the packet and, although different herbs grow to maturity at different times, you can expect to harvest your first herbs in just a few weeks.
Thanks for reading! I'm Michael — houseplant fanatic and your Pinterest plant guide.
Follow me on Pinterest for fresh updates 🌿



